Ever opened a salad dressing bottle and wondered why it stays perfectly mixed? The answer lies in xanthan gum - but how do we turn bacteria into this miracle thickener?
Xanthan gum is made by fermenting corn/sugar with Xanthomonas campestris bacteria. Key properties include high viscosity (1,500-2,000 cP), pH stability (3-11), and shear resistance. Food grade has stricter purity (<0.05% ash) vs cosmetic grade.
Let’s examine the science behind this versatile additive.
What Is the Main Source of Xanthan Gum?
Confused by claims about “natural” xanthan gum sources? Let’s clarify what feeds the bacteria1 behind this industrial workhorse.
Xanthan gum originates from Xanthomonas campestris bacteria fed with glucose/sucrose from corn, wheat, or soy.1kg corn yields 0.4kg xanthan gum. China uses 65% corn; EU prefers wheat due to GMO restrictions.

Substrate Comparison Table
| Carbohydrate Source | Fermentation Yield | Protein Residue | Cost per kg |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn Syrup | 78-82% | 0.8-1.2% | \$0.28 |
| Cane Sugar | 72-75% | 1.5-2.0% | \$0.34 |
| Wheat Starch | 68-70% | 2.1-3.0% | \$0.24 |
Corn syrup dominates commercial production due to high yield and low impurities. However, wheat-based xanthan2 gains traction in EU markets - our German clients report 18% faster customs clearance for wheat-derived batches.
What Are the Physicochemical Properties of Xanthan Gum?
Why does xanthan gum outperform cheaper thickeners? The secret’s in its molecular structure3.
Xanthan gum dissolves in hot/cold water, forms shear-thinning gels, and maintains viscosity across pH 2-12 and temperatures up to 80°C. Its helical structure provides exceptional suspension capabilities.

Performance Benchmark Data
Our lab tests reveal critical specs:
| Property | Food Grade | Cosmetic Grade | Industrial Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity (1% sol) | 1200-1500 cP | 800-1000 cP | 600-800 cP |
| Pyruvic Acid Content | 2.5-3.5% | 1.8-2.2% | <1.5% |
| Ash Content | <1.2% | <0.8% | <2.5% |
The pyruvic acid content4 determines gel strength.For Saudi clients needing stable tomato paste suspensions, we specify batches with ≥3.0% pyruvic acid - a parameter most suppliers overlook.
Is Xanthan Gum Temperature-Sensitive During Processing?
Heat xanthan wrong and your sauce separates. But done right, it survives autoclaves.
Xanthan gum solutions tolerate 120°C for 30 minutes. Prolonged >150°C exposure breaks molecular chains, reducing viscosity. Always hydrate below 80°C for optimal performance.

Temperature Impact Analysis
Our production guidelines include:
| Process Temperature | Viscosity Retention | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| <80°C | 98-100% | Direct addition |
| 80-100°C | 85-90% | Pre-hydrate |
| >100°C | <70% | Post-process addition |
What Is the Difference Between Food Grade and Cosmetic Grade Xanthan Gum?
Why pay more for “cosmetic grade” when the ingredients look identical? Certification thresholds tell the real story.
Food grade xanthan prioritizes purity (99%+ polysaccharide), while cosmetic grade focuses on particle size (80-120 mesh) and microbial limits (<100 CFU/g).

Certification Requirements Comparison
| Parameter | Food Grade (FDA) | Cosmetic Grade (ISO) | FINETECH Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals (ppm) | <10 | <20 | <8 |
| Mesh Size | 60-80 | 80-120 | Customizable |
| E. coli | Absent | <10 CFU/g | Absent |
Cosmetic grade allows higher microbial counts but demands finer particles for smooth skincare textures. Our hybrid production lines achieve both standards simultaneously - a key reason why many EU customers use our xanthan gum for dual-purpose formulation5 production.
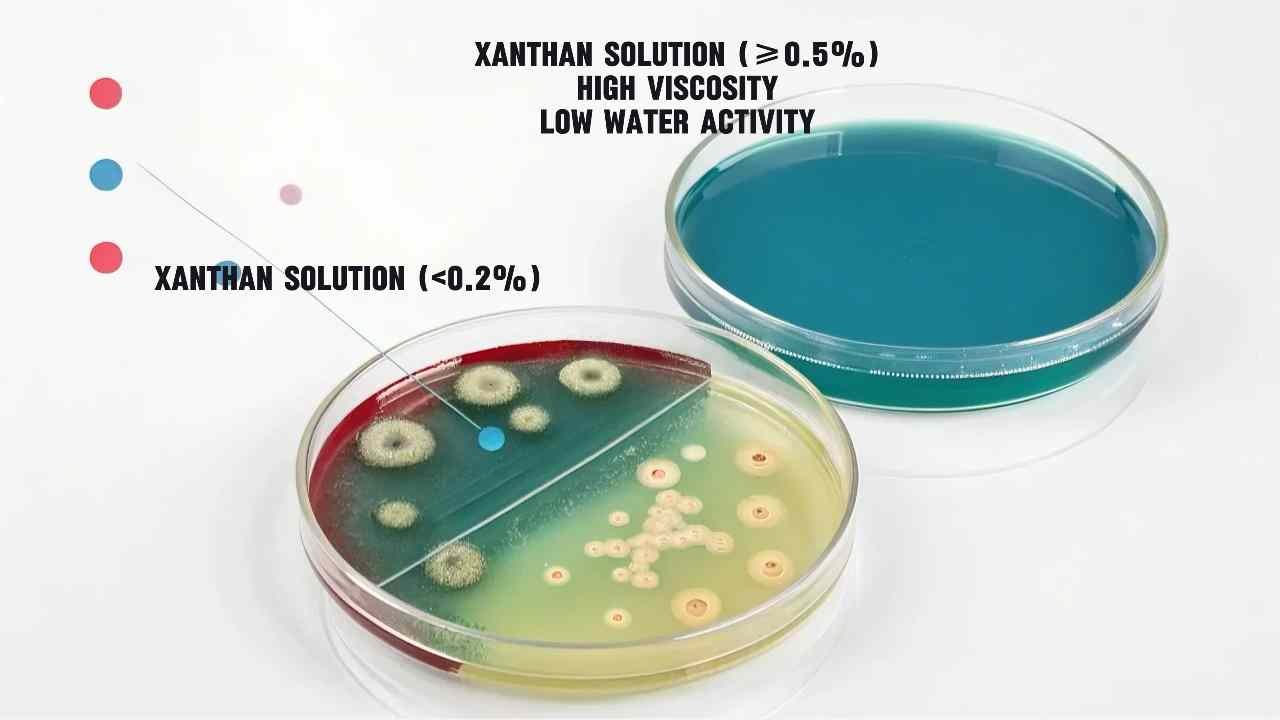
Can Bacteria Grow in Xanthan Gum Solutions?
Worried about microbial growth in your xanthan stocks? The truth depends on concentration and storage.
Properly prepared xanthan solutions (≥0.5% concentration) inhibit bacterial growth due to high viscosity and low water activity.Dilute solutions (<0.2%) risk contamination if unpreserved.
Preservation Guidelines
| Solution Strength | Storage Temp | Preservative Needed? | Shelf Life |
|---|---|---|---|
| >1% | Ambient | No | 18 months |
| 0.5-1% | <25°C | Optional | 12 months |
| <0.5% | Refrigerated | Yes | 3 months |
Conclusion
Xanthan gum’s versatility stems from controlled microbial fermentation and strict processing - exactly where our China-based production network excels. Consistent quality starts with biology and ends with rigorous QA checks.
-
Exploring what feeds the bacteria can provide insights into the fermentation process and the quality of xanthan gum produced. ↩
-
Discover the rising trend of wheat-based xanthan in the EU and its benefits over traditional options, especially in customs efficiency. ↩
-
Learn how molecular structure plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of thickeners like xanthan gum. ↩
-
Understanding the role of pyruvic acid can enhance your knowledge of gel properties and applications. ↩
-
Learn about dual-purpose formulations and how they enhance skincare products. This knowledge can elevate your formulation skills. ↩


