See "Riboflavin (B2)" on fortified food labels? Wonder why it's added? Let's quickly see why B2 is key for fortified foods and public health.
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) is vital for energy release from food, cell function, and growth. Fortification helps prevent deficiency, boosting public health via common foods like cereals and milk.
At FINETECH, we supply essential food additives like Vitamin B2. Understanding its role in fortification is important for our clients, who source ingredients for large-scale food production. Let's briefly cover B2 fortification.
What is the main job of Vitamin B2 in the body's energy cycle?
How does B2 actually help with energy? What's its core role? Let's quickly define Vitamin B2's main energy job.
Vitamin B2 (as FAD and FMN) is crucial for converting carbs, fats, and proteins into usable energy (ATP) by acting as a helper for many metabolic enzymes.
Vitamin B2 doesn't give energy directly. It acts as a component of two coenzymes: FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide)1 and FMN (flavin mononucleotide). These coenzymes are like essential worker bees for enzymes involved in:
- Breaking down macronutrients: Carbs, fats, and proteins from food.
- Electron Transport Chain2: The final stage of energy production (ATP synthesis) in cells. FAD is vital here.
- Activating other B vitamins3: B2 helps convert B6 and folate into their active forms.
B2's Energy Cycle Role:
| B2 Form | Key Function | Result |
|---|---|---|
| FAD/FMN | Coenzyme for energy-producing enzymes | Enables ATP production |
| FAD | Key in electron transport chain | Efficient energy release |
| FMN/FAD | Helps activate other B vitamins | Supports overall metabolism |
Without enough B2, your body can't efficiently turn food into fuel.
How does Vitamin B2 in cereals and milk improve public nutrition?
Why add B2 to everyday foods like cereal and milk? How does this help everyone? Let's see B2 fortification's public health impact.
Fortifying staples like cereals and milk with B2 ensures wider populations get enough, especially those with poor diets or higher needs, reducing deficiency risks and boosting overall nutritional status.

Fortification4 is a public health strategy. Many people might not get enough B2 from diet alone, especially if they don't eat many B2-rich foods (like dairy, organ meats, some green veggies).
- Reaching Many People: Cereals and milk are widely consumed by various age groups. Fortifying them makes B2 accessible.
- Replacing Losses: Grain processing (milling for white flour) removes natural B2. Fortification adds it back.
- Targeting Vulnerable Groups: Children, pregnant women, elderly, and low-income individuals might be at higher risk of deficiency. Fortified staples help them.
Public Health Benefits:
| Fortification Aspect | How It Improves Nutrition |
|---|---|
| Wide Consumption | B2 reaches diverse populations |
| Replaces Losses | Counters B2 lost in grain processing |
| Supports Vulnerable | Helps those at higher risk of deficiency |
| Easy Access | No need for special foods/supplements |
What health problems from Vitamin B2 deficiency does fortification prevent?
What happens if you don't get enough B2? What issues does fortification stop? Let's look at B2 deficiency problems.
B2 deficiency (ariboflavinosis) can cause sore throat, cracked lips/mouth corners (cheilosis), skin issues (dermatitis), red tongue, fatigue, and eye problems. Fortification helps prevent these.
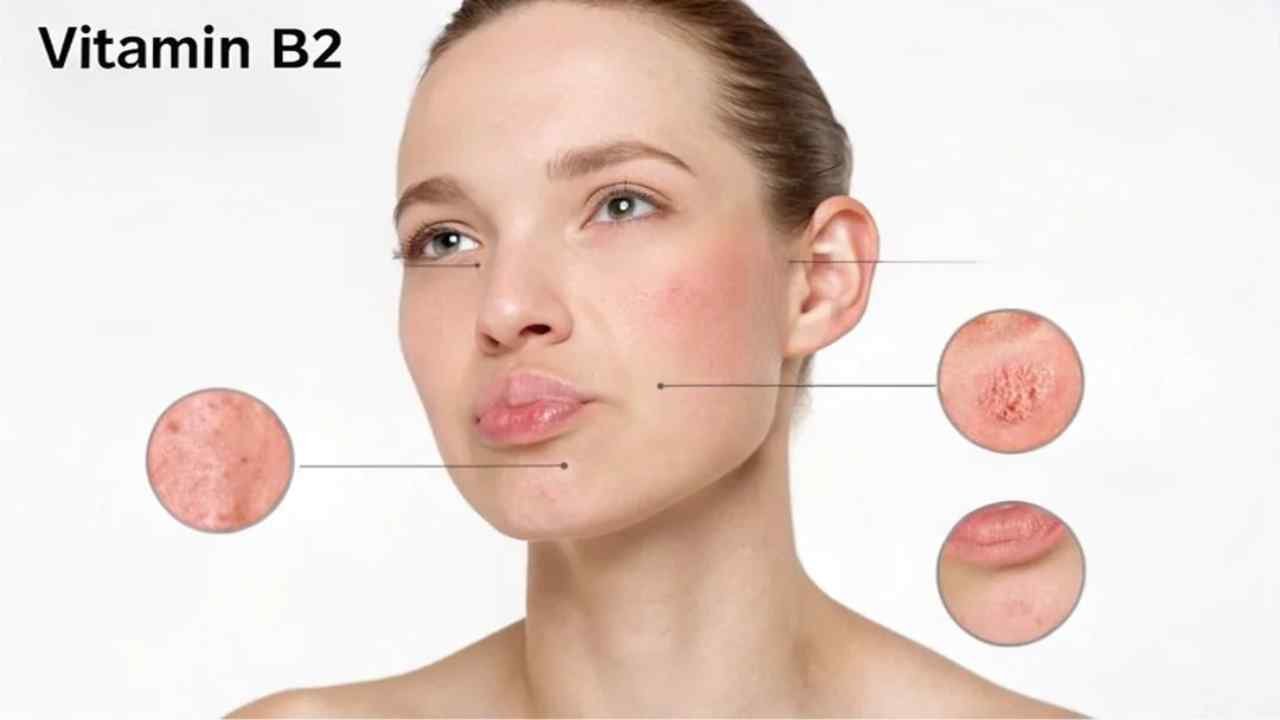
Lack of B2 affects tissues that turn over quickly, like skin and mucous membranes. Early signs:
- Mouth/Lips: Sore throat, redness/swelling of mouth/tongue (magenta tongue), cracks at mouth corners (angular cheilitis), chapped lips (cheilosis).
- Skin: Greasy, scaly skin rashes (seborrheic dermatitis), especially around nose, ears, scalp.
- Eyes: Bloodshot eyes, light sensitivity, itching, burning.
- General: Fatigue, weakness.
- Severe: Anemia (if B2 deficiency5 impairs iron use), nerve issues (rare unless severe).
Fortification aims to prevent these by ensuring a baseline B2 intake for most people.
Deficiency Symptoms Prevented:
| Area Affected | Common B2 Deficiency Signs |
|---|---|
| Mouth/Lips | Sore throat, Cracked lips/corners |
| Skin | Scaly rashes |
| Eyes | Redness, Light sensitivity |
| General | Fatigue |
Which foods and drinks are commonly enriched with Vitamin B2?
Where can you find added B2? Which products are often fortified? Let's list common B2-enriched foods.
Commonly B2-enriched foods: breakfast cereals, white flour/bread/pasta, milk/dairy alternatives (soy/almond milk), infant formulas, and some energy drinks or nutritional beverages.

Manufacturers add B2 to foods that are:
- Widely consumed: To reach many people (e.g., bread, cereals, milk).
- Processed (losing natural B2): White flour/rice products.
- For specific needs: Infant formulas ensure babies get enough.
- Functional foods: Energy drinks may add it for its role in energy metabolism.
Examples of B2 Fortified Products:
| Food Category | Reason for Fortification |
|---|---|
| Cereals, Breads, Pasta | Replace processing losses, broad reach |
| Milk, Dairy Alternatives | Boost intake, common staple |
| Infant Formulas | Ensure adequate B2 for growth |
| Nutritional Drinks | Support energy metabolism claims |
How does the demand for healthy foods impact the Vitamin B2 market?
Do health trends boost B2 use? How does the "healthy food" focus affect B2 demand? Let's see the market impact.
Growing consumer demand for fortified, functional, and "healthy" foods (e.g., plant-based milks, sports nutrition) drives increased use of Vitamin B2 as a value-adding, health-associated ingredient.

The shift towards healthier eating and functional foods boosts the B2 market:
- Fortification Trend: More foods are fortified beyond basic staples to appeal to health-conscious consumers.
- Plant-Based Alternatives: Plant milks (soy, almond) are often fortified with B2 to match dairy milk's profile.
- Sports Nutrition/Energy Products: B2 is added for its role in energy metabolism, meeting demand from active consumers.
- Dietary Supplements: General wellness trend increases demand for B-complex and individual B vitamin supplements.
- "Clean Label" & Awareness: Consumers are more aware of vitamin benefits, creating a pull for fortified options.
Market Drivers for B2:
| Consumer Trend | Impact on B2 Demand |
|---|---|
| Health & Wellness Focus | Increases use in fortified/functional foods |
| Plant-Based Diets | Fortification of dairy alternatives |
| Sports & Active Nutrition | Demand for energy metabolism support |
| Increased Vitamin Awareness | Drives supplement and fortified food sales |
This rising demand ensures a steady market for quality B2 suppliers like FINETECH.
Conclusion
Vitamin B2 fortification is vital for energy metabolism and public health, preventing deficiency by enriching common foods. Growing health consciousness further boosts its demand and market importance.
-
Exploring FAD's role in metabolism will enhance your knowledge of energy production and the importance of coenzymes in biochemical processes. ↩
-
Understanding the Electron Transport Chain is crucial for grasping how energy is produced in cells, making it a key topic for anyone interested in biochemistry. ↩
-
Learning about how Vitamin B2 activates other B vitamins can provide insights into the interconnectedness of nutrients and their roles in health. ↩
-
Exploring this resource will provide insights into how fortification improves public health and nutrition. ↩
-
Understanding B2 deficiency can help you recognize symptoms and seek appropriate treatment. ↩


